Types of anti-fall safety harness: regulations and classification
When working at height it is essential to choose the right safety harness, depending on the situation.
Reference anti-fall regulations
- EN341 Rescue descent device
- EN353-1 Sliding fall arrest devices on rigid anchor line
- EN353-2 Sliding fall arrest devices on flexible anchor line
- EN354 Lanyards
- EN355 Energy absorbers
- EN358 Restraint/Restraint Belts and Restraint Lanyards
- EN360 Retractable fall arresters
- EN361 Fall arrest harnesses
- EN362 Connectors
- EN567 Blockers
- EN795 Anchoring devices
- EN813 Seat harnesses
- EN1496 Lifting rescue harnesses
- EN1497 Rescue harnesses
- EN1498 Rescue tapes
- EN1891 Braided ropes with sheath, semi-static
- EN12278 Pulleys
Categories of work at height: fall arrest, rescue, work in suspension or restraint
Anti-fall equipment
Equipment used to arrest a worker's fall from an elevated position. The usual anti-fall system is made up of the following elements:
- Anchoring devices.
- Anti-fall body harness.
- Anti-fall connection devices.
Suspended work
Designed to allow operators to work suspended without the support of their feet while having the mobility of their hands.
The usual suspension system is made up of the following elements:
- Anchoring devices.
- Full body anti-fall harness.
- Two ropes.
- One equipped with a descender/blocker.
- One equipped with a sliding kill switch.
Rescue
Rescue and evacuation of an operator injured at height is a mandatory consideration.
The usual rescue system is made up of the following elements: Rescue and evacuation device.
Potioning at work
Equipment that holds an operator in his workplace, while having the mobility of his hands.
The usual work positioning system is made up of the following elements:
- Anchoring devices.
- Full body harness with positioning belt.
- Joining devices (positioning lashing element).
Fastening work
Equipment used to prevent the worker from being in a position at risk of falling.
The usual fastening system is made up of the following elements:
- Anchoring devices.
- Restraint belt or full body harness.
- For the purpose of this Regulation, the following definitions shall apply:.
What kind of death harness should I choose?
A harness is the main component of a fall arrest system. Designed to support the body and stop the fall, it distributes the forces generated and keeps the worker in head-up suspension.
How do I choose the right harness for my type of work?
- If the work only requires the person to be held in order not to fall, a harness with 1 or 2 fixing points will suffice. One-point harnesses carry only one dorsal restraint point. 2 point harnesses are equipped with 1 dorsal anchorage point and 1 sternal (front) anchorage point.
- When the work requires the user to work with the hands free, a harness must be selected that allows holding: this type can have back and outside points, but older ones must be equipped with 2 side anchorage points for positioning.
- Suspension work requires technical complements that allow maintaining the position of the body, which is associated with the rope descent equipment connected to the abdominal part of the belt.
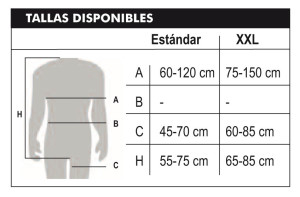
Anti-fall harness size: one size harness and XXL harness.
Most harnesses on the market are one size fits all, which is true for most workers. But there are also harnesses that allow another range of sizes, so the ability to adjust the harness correctly is essential for comfortable and safe use:
Weight supporting the safety harness
Most harnesses are certified for 100 kg. This does not mean that if the user weighs more than 100 kg that they will fall; This means that the harnesses were tested with a mass of 100 kg. But if the person who is going to use it weighs more than 100 kg, it is recommended to choose one that is certified for 140 kg:
 80071-XL |
 80072 |
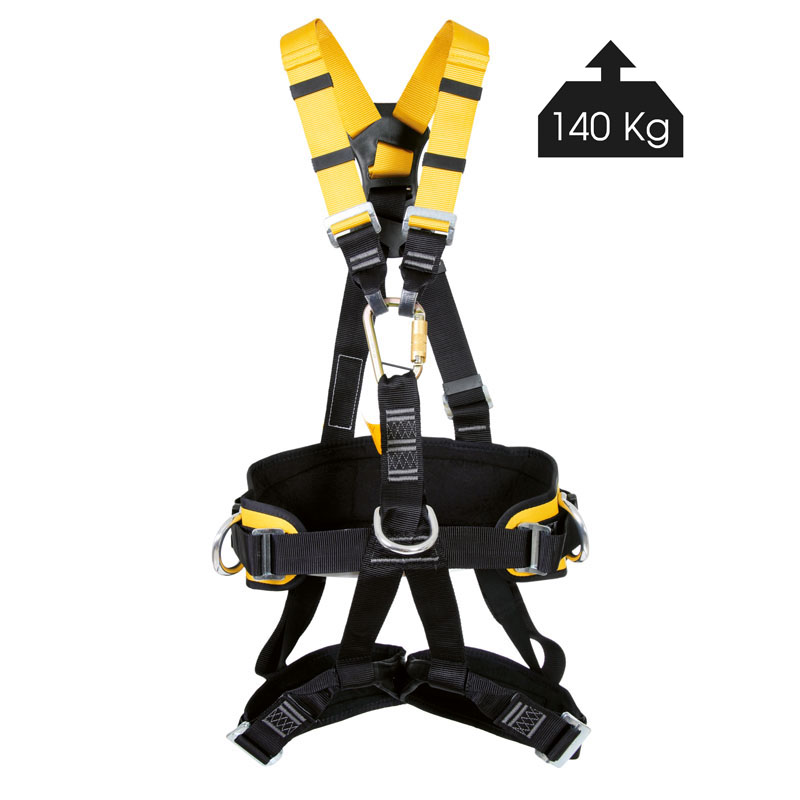 80076 |
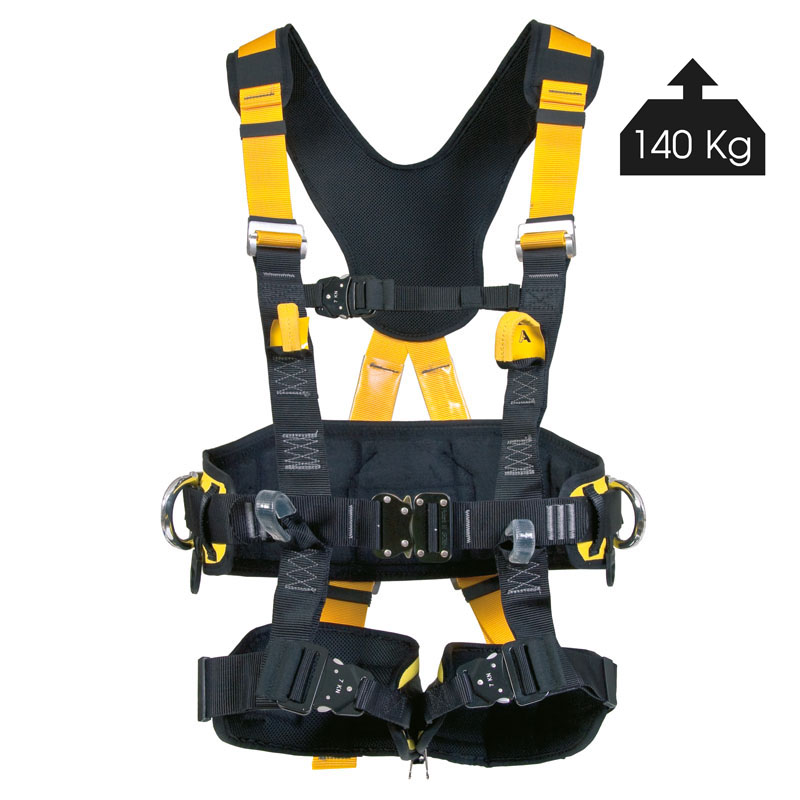 80082 |
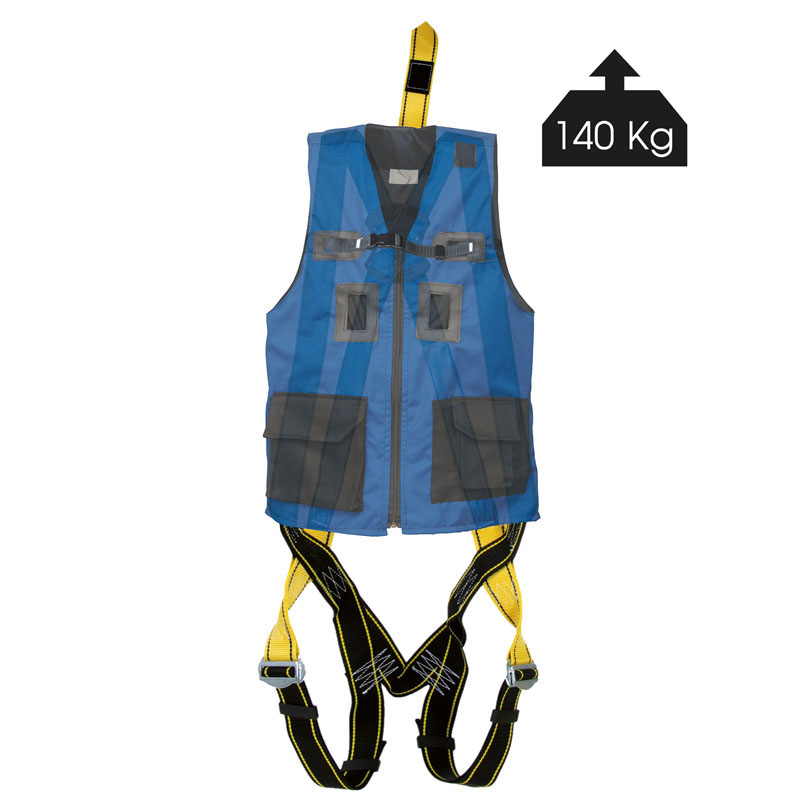 80084 |
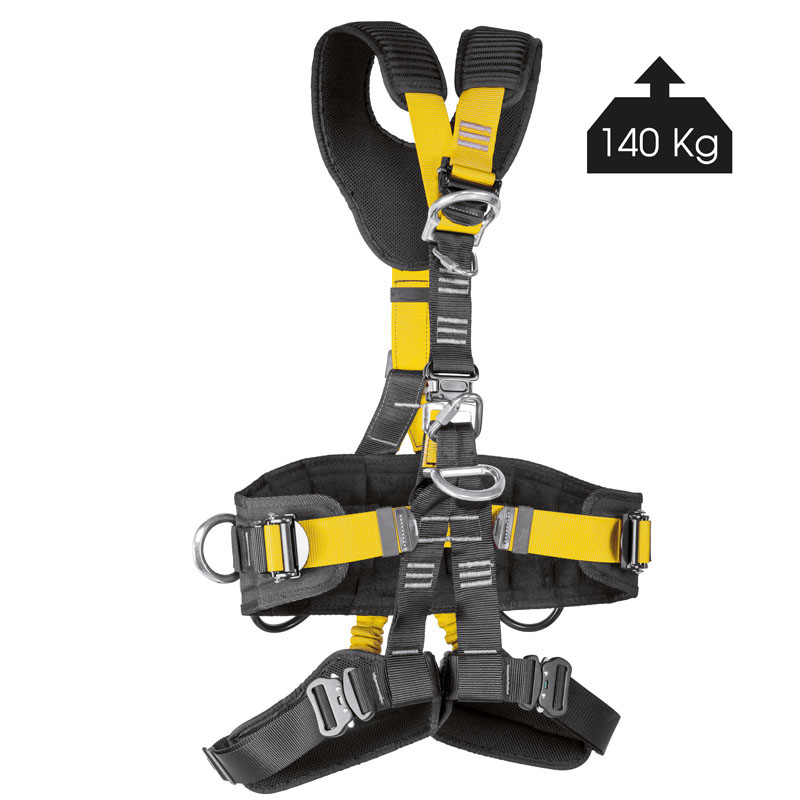 80086 |
Other European Standards related to fall arrest equipment
While EN 361:2002 refers to the full body harness, there are other EN standards to consider for other fall arrest equipment, including:
- EN361 Fall arrest harnesses
- EN813 Seat harnesses
- EN358: Positioning harnesses
- EN1496 Lifting rescue harnesses
- EN1497 Rescue harnesses
Instructions and annual inspection of fall protection equipment. What is the expiration date of a safety harness?
Like all PPE, fall arrest equipment must always have a user manual attached, along with a PPE registration sheet. All equipment must have an explicit guide for use, maintenance and inspection.
Always consult the manufacturer's instructions to know the frequency of inspections and their useful life.
An exceptional event could reduce the useful life of the product to a single use; For example, if the equipment is dropped, exposed to chemicals, extreme temperatures, sharp edges, heavy load, etc.
The user must inspect the equipment periodically to check for damage and/or deterioration. In addition to checks before and during use, a regular in-depth inspection by a competent inspector must be carried out at least once every 12 months.
The frequency of inspection should be governed by the type and intensity of use. To better track your team, it is preferable to assign each team to a single user so that they know its history. The results of the checks should be recorded on an equipment control card.
This document must allow the registration of the following data: type of equipment, model, name and contact of the manufacturer or distributor, identification (serial number), year of manufacture, date of purchase, date of first use, name of the user, all relevant information, for example, maintenance and frequency of use, history of periodic inspections (date, comments and whether problems have been reported, name and signature of the competent person carrying out the inspection, expected date of the next inspection).
The periodic review method could be carried out as follows:
- Inspect the belts, checking for damage or cuts.
- Check all metal fittings for any damage or rust. Inspect for broken or torn areas.
- Check all plastic accessories.
- Check all points of the PPE.
- Keep all inspection details on the control card.
- Check it's not punctured.
- Check the readability of product markings.